Graph: Shortest Path Problems
2021-05-11
0. 前言
从我们打开浏览器,输入网站,到看到网页这个过程中,发生了很多事情。
我们的设备(电脑)需要把数据经过多个 router 发送给网站,然后网站穿给我们的数据又经过多个 router 到达电脑的浏览器。
mac 用户可以用
traceroute <website address>得到详细的 routing 信息。
每个 router 都和一个或多个 router 相连,每天的不同时间访问同一个网站,routing 很有可能是不同的。
我们可以把 network of routers 用一个 graph with weighted edges 来表示,edge 的 weight 表示的是两个 router 之间连接的时间。
我们要解决的问题是:找到从 A router 到 B router 之间时间最短的那条路径。
1. Shortest Path Problems
我们在讲 BFS 的时候,解决的是一个类似的问题:Word Ladder(找到从 A 变成 B 的最短路径)。
Word Ladder 里面的 edge 是没有 weight 这个属性的,假如我们这个 routing 的问题中去掉了 weight,就跟 Word Ladder 的问题一模一样~
最短路径问题有两类:
- Weighted Graph - Word Ladder
- Unweighted Graph - Routing
2. Dijkstra’s Algorithm
我们用来解决最短路径问题的算法叫做 Dijkstra’s Algorithm(戴克斯特拉算法)
这个算法的特点是,你只要给定 starting node,它能帮你找到 starting node 到所有其他 node 的最短距离,类似 BFS 的返回结果。
注意:这个算法只有在 edge weight 非负数的情况下才能用。
It is important to note that Dijkstra’s algorithm works only when the weights are all positive. You should convince yourself that if you introduced a negative weight on one of the edges to the graph that the algorithm would never exit.
逻辑
-
我们用 dist 这个属性来记录从 starting node 到其他 node 的距离,dist 代表从 starting node 到当前 node 的 total weight。
-
由于图中的每个 node 都要访问,我们用 priority queue 来决定访问 node 的次序,priority queue 的排列是基于 dist 这个属性的。
-
我们把每个 node 的 dist 初始值设的非常大,算法结束时每个 node 的 dist 都会成为正确的值。
复习
Priority Queue 是基于 Binary Heap 实现的,我们当时实现的那个 PQ 和 Dijkstra 算法 的 PQ 有一些不同。
- Priority Queue class 存 tuples of key, value pairs, 在 Dijkstra 算法中,Priority Queue 的 key 必须和 node/vertex 的 key 一样;
- tuple 里面的 value 是用来决定优先级的,我们用 node/vertex 的 distance 作为优先级;
- 我们有个额外的 method -
decreaseKey,当一个 node 已经在 queue 里面时,这个 method 会被调用,来减少 node 的 dist,因为 dist 变少了,所以这个 node 也会被排到优先队列的前面。
Code
from pythonds.graphs import PriorityQueue, Graph, Vertex
def dijkstra(aGraph,start):
pq = PriorityQueue()
start.setDistance(0)
pq.buildHeap([(v.getDistance(),v) for v in aGraph])
while not pq.isEmpty():
currentVert = pq.delMin()
for nextVert in currentVert.getConnections():
newDist = currentVert.getDistance() \
+ currentVert.getWeight(nextVert)
if newDist < nextVert.getDistance():
nextVert.setDistance( newDist )
nextVert.setPred(currentVert)
pq.decreaseKey(nextVert,newDist)
2. 算法图解
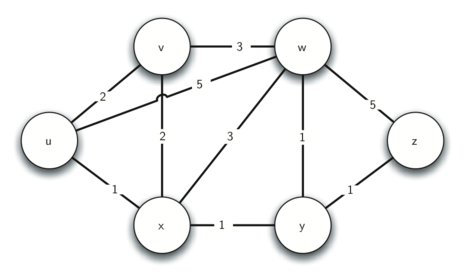
1. 准备工作
-
Starting node:
u -
u有三个邻接 node:v,w,x -
三个邻接 node 的初始 dist 是
sys.maxint -
新的 dist 是它们跟 start node 之间的 edge 重量
v: d = 2
w: d = 5
x: d = 1
-
我们把这三个 node 的 predecessor 都设为
u -
dist 是 priority queue 的 value
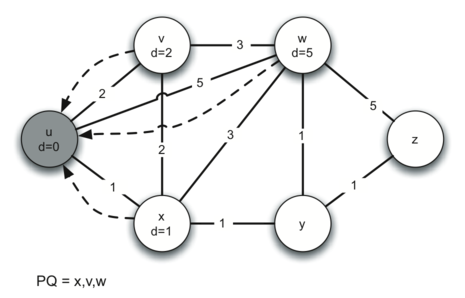
2. while loop
因为 x 的 dist 最小,它在优先队列的最前面,所以我们先看 x 的邻接 node - u, v, w, y.
我们会看一下每个邻接 node 的 dist,从 x 到这些 node 的距离是否比之前已知的 dist 要小,假如是的话就更新 dist。
我们发现 y 的 dist 是初始值 sys.maxint,现在更新为 2 (start node 到 x 再到 y 的距离)。
u 和 v 的距离不需要更新。
w 的距离本来是 5,现在可以减少到 4,我们也更新一下,同时把 w 的 predecessor 改成 x。
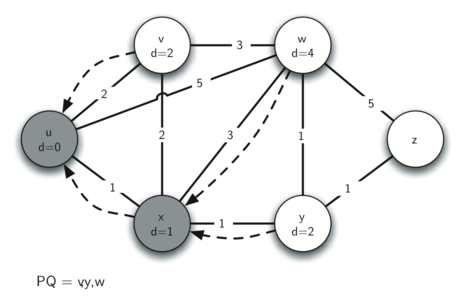
3. 访问 v
根据优先队列的顺序,我们访问 v 。
v 的邻接 node 没有什么要改变的 - dist 不需要更新,predecessor 也不需要更新。
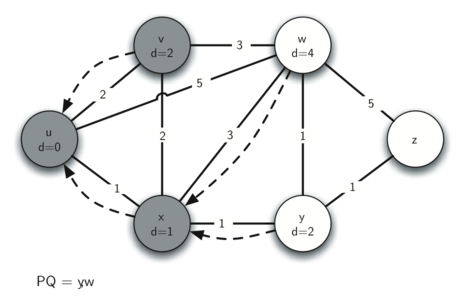
4. 访问 y
我们可以更新 w 和 z 的距离和 predecessor。
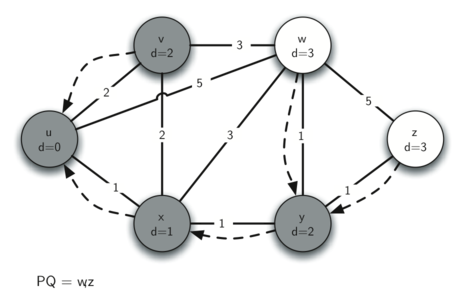
5. 访问 w
没有要改的。
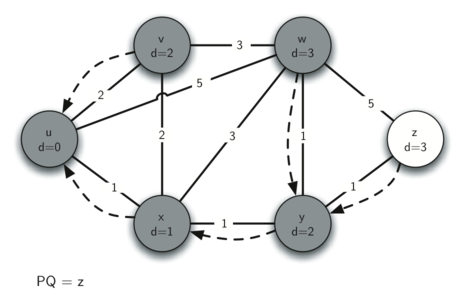
6. 访问 z
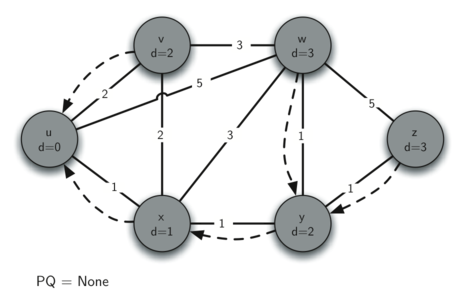
没有要改的,priority queue 为 empty,跳出循环。
4. 算法分析
局限
- 不支持负数 weight;
- 你必须有完整的图才能开始计算;
The implication of this is that every router has a complete map of all the routers in the Internet.
不过呢,有其他的算法可以在图不完整的时候进行计算,比如 “distance vector” routing algorithm.
复杂度
-
build priority queue - O(V)
每个 node 都访问一次
-
while loop - O(VlogV)
每个 node 都访问一次 - O(V)
在 while loop 里面的 delMin - O(logV)
-
for loop - 𝑂(Elog𝑉)
每个 edge 一次 - O(E)
for loop 里面的 decreaseKey - 𝑂(log𝑉)
总共的时间复杂度:
O(V)+O(VlogV)+𝑂(Elog𝑉)
= 𝑂((𝑉+𝐸)log(𝑉)).